Friday, December 2, 2011
Monday, November 21, 2011
Monday, October 10, 2011
Idiopathic Bullous Emphysema (Vanishing Lung Syndrome)
Wednesday, September 14, 2011
QR Codes
QR Codes could be used in Radiology as follows:
1. added to posters and other marketing paraphenalia
2. add to the bottom of reports to communicate any info
3. use it to give patients directions to practices via google maps
4. use for roster links
If you (like me) need some more info, here it is:
---Generate a QR code (pretty easy)
http://qrcode.kaywa.com/
http://invx.com/
---Read a QR code
your Android or iOs device may have a QR scanner built in, otherwise head to the Android market or iPhone app store and search for QR code scanner
---More info
http://www.labnol.org/internet/tools/qr-codes-share-text-inside-images/3867/
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-qr-code.htm
--Marketing Advantages:
http://www.socialmediaexaminer.com/how-qr-codes-can-grow-your-business/

1. added to posters and other marketing paraphenalia
2. add to the bottom of reports to communicate any info
3. use it to give patients directions to practices via google maps
4. use for roster links
If you (like me) need some more info, here it is:
---Generate a QR code (pretty easy)
http://qrcode.kaywa.com/
http://invx.com/
---Read a QR code
your Android or iOs device may have a QR scanner built in, otherwise head to the Android market or iPhone app store and search for QR code scanner
---More info
http://www.labnol.org/internet/tools/qr-codes-share-text-inside-images/3867/
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-qr-code.htm
--Marketing Advantages:
http://www.socialmediaexaminer.com/how-qr-codes-can-grow-your-business/
Thursday, August 18, 2011
Gd Guidelines
http://radiologymri.blogspot.com/2011/08/gadolinium-guidelines.html
Radiology May 17, 2011
Thanks, Robert.
Radiology May 17, 2011
Thanks, Robert.
Monday, August 15, 2011
Grade II Sprain Interosseous component of Lisfranc Ligament
Wednesday, August 3, 2011
Saturday, July 30, 2011
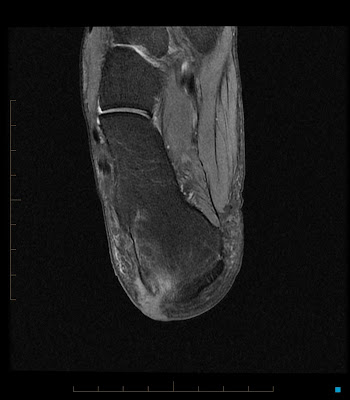
Tibial Tunnel Cyst post ACL Recon (II)
Labels:
ACL Reconstruction,
Knee,
MRI,
MSK,
Tibial Tunnel Cyst
Monday, June 20, 2011
Thursday, June 9, 2011
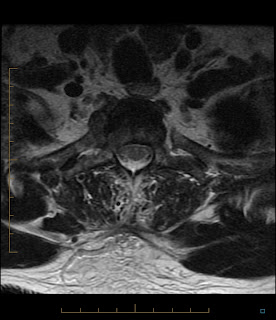
Costovertebral Arthritis ? Septic
Labels:
Costovertebral,
MRI,
MSK,
Septic Arthritis,
Spine
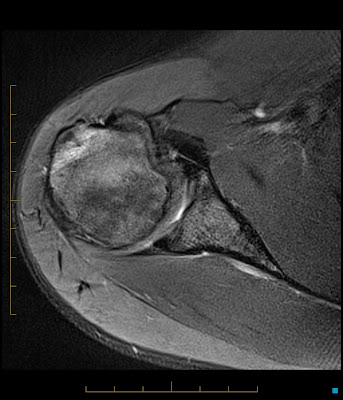
Reverse Hill Sachs
Labels:
Hill-Sachs,
MRI,
MSK,
Reverse Hill Sachs,
Shoulder
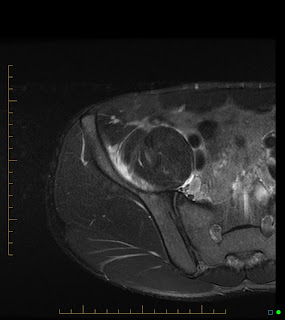
Quadrilateral Space Syndrome
Monday, May 16, 2011
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 9. Elbow
- Anatomical Variants
- pseudo defect of trochlea
- transverse trochlea ridge
- pseudo defect of capitellum (post on coronal)
- Valgus injury (throwing) - tension medial side, compression lateral side
- "T sign" - partial tear anterior bundle MCL distally
- Medial Anatomy - PT, FCR, FDS
- Lateral Anatomy - ECRB (most common tendon involved), EDC, ECU
- Lateral - 3 ligaments - LCL, LUCL (attaches to supinator crest of ulna distally), annular ligament
- Biceps tear - if partial need to state wether under or over 50%
- Lacertus fibrosis - medial to biceps on axial; prevents proximal "slingshot" of torn biceps
- Anconeus epitochlearis
Labels:
Elbow Variants,
Normal Variant,
Pearls,
Stoller
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 8. Wrist
- Coronal plain most NB
- GRE for TFCC
- Extrinsic ligaments ["volar extrinsic ligaments"]- rarely torn (RSC, RLT, RSL)
- SL Ligament complex - 3 components - dorsal (strongest), middle (weakest), volar
- LT Ligament complex - 3 components - d, m , v(strongest)
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 7. Muscle
- Direct Injury - contusion, laceration, haematoma
- Indirect injury- strain or tear
- Myositis Ossificans - peripheral calcification - do a CT
- DOMS
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 6. Hip
- Normal sulcus - Posteroinferior sublabral sulucs, Transverse Ligament Labral Sulcus, Perilabral Sulcus
- Stellate Lesion - supra-acetabular fossa; more prom. in teens; normal thinning
- GRE for chondrocalcinosis
- AVN Grading - Ficat and Arlet
- TOH -- actually all stress # (subchondral) or insufficiency; repeat MRI in 3 months to exclude AVN (<10%) and document resolution of oedema
- Labral Tears - most are chondrolabral or longitudinal
- Iliofemoral ligament - thickening = inflammatory response secondary to degeneration
- Lig. teres hypertrophy = DDH
- Labral hypertrophy = DDH
Thursday, May 5, 2011
Grading of Disc Related Nerve Root Compression (Pfirrmann et al)
- Grade 0 (normal) - No compromise of the nerve root is seen. There is no evident contact of disk material with the nerve root, and the epidural fat layer between the nerve root and the disk material is preserved.
- Grade 1 (contact) - There is visible contact of disk material with the nerve root, and the normal epidural fat layer between the two is not evident. The nerve root has a normal position, and there is no dorsal deviation.
- Grade 2 (deviation) - The nerve root is displaced dorsally by disk material.
- Grade 3 (compression) - The nerve root is compressed between disk material and the wall of the spinal canal; it may appear flattened or be indistinguishable from disk material.
February 2004 Radiology, 230, 583-588.
Labels:
DIsc protrusion,
Grading,
MRI,
Nerve Root Compression Grading
Monday, May 2, 2011
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 5. Mid and Forefoot
- 1st MTP Anatomy p166
- Skimboarder's Toe - "reverse turf toe" - dorsal plate injury
- Lisfrance ligament - medial cuneiform to 2nd MT base
- dorsal, interosseus and plantar components - fail from dorsal to plantar
- no interosseus ligament between 1st and 2nd MT bases
- Baxter's Neuropathy
- Ab. Digiti Mini Atrophy; check nerve entrapment foot
- Adventitial Bursitis
- no anatomic bursa in foot
- at pts of frictional wear,
- may present as mases
- plantar 1st and 5th, hallux valgus common
Labels:
Adventiial bursitis,
Baxter's Neuropathy,
Conference,
Forefoot,
Lisfranc,
Midfoot,
Skimboarder's Toe,
Stoller
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 4. Ankle
- NB: anterior process talus; lateral process calcaneus (snowboarders)
- Subtalar joint - anterior, middle, posterior facets
- Lateral gutter -- a 3D space between AITFL/PITFL and ATFL/PTFL
- Posterior ankle ligaments - Transverse Tib-Fib Lig, PITFL, Tibial Slip, PTFL
- Anterolateral impingement (soft tissue related to antero-lat gutter) vs Ant. impingement (bony)
- Soft Tissue Impingement
- Anterolateral (ATFL and AITFL related to partial or completer tear)
- Syndesmotic
- Posterior (PTFL -- myxoid)
- Spring (Calcaneonavicular ligament)
- Lateral/Intermediate/Superomedial
- Axial - int. and lat.; slice up - superomedial
- Coronal - next to TP
- POP Syndrome
- # or displacement of Os peroneum
- Ass. Peroneus Longus Tear
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Post. Tibial N. compression
- 4 Plantar Muscles - (Med) Ab. Hallucis, Fl. Dig. Brevis, Quadratus Plantae, Ab. Digiti Minimi
- Subtalar ligaments
- subtalar interosseus - medial (coronal)
- cervical - lateral and anterior (coronal and sag)
- intermediate root extensor retinaculum - post. to cervical (sag)
- OLT Stages
- Tennis Leg - ruptured crura; fascia
Labels:
Ankle,
Conference,
Pearls,
POPS,
Stoller,
Tennis Leg
Sunday, April 17, 2011
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 3. Knee
- Trochlear groove - assess on sag.
- Meniscofemoral and meniscotibial (coronary) recesses.
- Horizontal tear - must extend to apex (sag).
- Flap tear - one type that looks horizontal but extends short of apex creating small inferior leaf.
- Flap tear -- vertical configuration, but inner 1/3 (sag).
- Vertical/longitudinal tear - outer 1/3 (sag).
- Menisco-capsular separation -- two scenarios
- ACL with tear of periph of post. horn lat. meniscus (fluid betw. capsule and periph. of post. horn).
- MCL tear with meniscotibial lig. tear.
- Posterolat. corner -- review on sag and axial.
- SONK -- almost all cases are probably insufficiency fractures
- CMP - MRI adaptation of Outerbridge classification; describe rather than classify; ICRS classification.
- MPFL - slice above proximal origin of MCL, tears at femur
- Patella tendinosis - best on GRE.
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 2.Shoulder
- Anterior band of IGHL can have high attachment -- 3rd structure on axial (in addition to labrum and MGHL).
- Sublabral foramen (antero-superior); sublabral sulcus (superior)
- Hill-Sachs - position - where articular cartilage in NOT; at level of footprint on axial (1st two slices).
- MGHL - "squiggly" on Sag.
- Patterns of glenoid sclerosis.
- Anteroinferior labrum -- assess 1st -- spectrum of injury
- Perthes - labral tear, minimal displacement, intact periosteum
- ALPSA - labral tear and medial displacement of IGLLC, medially stripped but intact periosteum (NB POLPSA)
- GLAD - labral tear (partial), no detachment, chondral defect, intact periosteum
- Bankart - avulsion of IGLLC (anterior and medial), disruption of scapula perisoteum
- SGHL/CHL -- "Biceps pulley" -- look on Sag
- HAGL -- anterior band IGHL tear (+BHAGL) aot RHAGL or PHAGL -- post. band
- GAGL
- "Wave Sign" -- massive RC tear - repairable acute tear without scarring
Pearls from Stoller Macau April 2011 - 1.Technique
- Zoom in to see detail.
- Every series should contain a plain T1.
- GRE/T2* -- for shoulders and knee at least -- useful for chondrocalcinosis, PVNS, blood
- Hip -- should include sag
- Hip - one large FOV series
- Ankle -- NB ant. process of calcaneus and lateral process of talus
Sunday, March 27, 2011
Thursday, March 10, 2011
Caton Deschamps Index
http://radiopaedia.org/cases/caton-deschamps-index
Methodology slightly different to "Patella Height Ratio" here:
MR Imaging of Patellar Instability: Injury Patterns and Assessment of Risk Factors, Radiographics July 2010
Methodology slightly different to "Patella Height Ratio" here:
MR Imaging of Patellar Instability: Injury Patterns and Assessment of Risk Factors, Radiographics July 2010
Wednesday, March 2, 2011
Baastrup's Disease
Iliopsoas Muscle Tear
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




































 i
i